MLA Tables, Figures, and Examples

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The purpose of visual materials or other illustrations is to enhance the audience's understanding of information in the document and/or awareness of a topic. Writers can embed several types of visuals using most basic word processing software: diagrams, musical scores, photographs, or, for documents that will be read electronically, audio/video applications. Because MLA style is most often used in the humanities, it is unlikely that you will include raw scientific data in an MLA-style paper, but you may be asked to include other kinds of research in your writing. For additional information on writing a research paper in MLA style, visit the MLA Style Center’s page on Formatting a Research Paper.
General guidelines
- Collect sources. Gather the source information required for MLA documentation for the source medium of the illustration (e.g. print, Web, podcast).
- Determine what types of illustrations best suit your purpose. Consider the purpose of each illustration, how it contributes to the purpose of the document and the reader's understanding, and whether the audience will be able to view and/or understand the illustration easily.
- Use illustrations of the best quality. Avoid blurry, pixilated, or distorted images for both print and electronic documents. Often pixelation and distortion occurs when writers manipulate image sizes. Keep images in their original sizes or use photo editing software to modify them. Reproduce distorted graphs, tables, or diagrams with spreadsheet or publishing software, but be sure to include all source information. Always represent the original source information faithfully and avoid unethical practices of false representation or manipulation (this is considered plagiarism).
- Use illustrations sparingly. Decide what items can best improve the document's ability to augment readers' understanding of the information, appreciation for the subject, and/or illustration of the main points. Do not provide illustrations for illustrations' sake. Scrutinize illustrations for how potentially informative or persuasive they can be.
- Do not use illustrations to boost page length. In the case of student papers, instructors often do not count the space taken up by visual aids toward the required page length of the document. Remember that texts explain, while illustrations enhance. Illustrations cannot carry the entire weight of the document.
Labels, captions, and source information
Illustrations appear directly embedded in the document, except in the case of manuscripts that are being prepared for publication. (For preparing manuscripts with visual materials for publication, see Note on Manuscripts below.) Each illustration must include a label, a number, a caption and/or source information.
- The illustration label and number should always appear in two places: the document main text (e.g. see fig. 1) and near the illustration itself (Fig. 1).
- Captions provide titles or explanatory notes (e.g., Van Gogh’s The Starry Night)
- Source information documentation will always depend upon the medium of the source illustration. If you provide source information with all of your illustrations, you do not need to provide this information on the Works Cited page.
MLA documentation for tables, figures, and examples
MLA provides three designations for document illustrations: tables, figures, and examples (see specific sections below).
Tables
- Refer to the table and its corresponding numeral in-text. Do not capitalize the word table. This is typically done in parentheses (e.g. "(see table 2)").
- Situate the table near the text to which it relates.
- Align the table flush-left to the margin.
- Label the table 'Table' and provide its corresponding Arabic numeral. No punctuation is necessary after the label and number (see example below).
- On the next line, provide a caption for the table, most often the table title. Use title case.
- Place the table below the caption, flush-left, making sure to maintain basic MLA style formatting (e.g. one-inch margins).
- Below the title, signal the source information with the descriptor "Source," followed by a colon, then provide the correct MLA bibliographic information for the source in note form (see instructions and examples above). If you provide source information with your illustrations, you do not need to provide this information on the Works Cited page.
- If additional caption information or explanatory notes is necessary, use lowercase letters formatted in superscript in the caption information or table. Below the source information, indent, provide a corresponding lowercase letter (not in superscript), a space, and the note.
- Labels, captions, and notes are double-spaced.
Table Example
In-text reference:
In 1985, women aged 65 and older were 59% more likely than men of the same age to reside in a nursing home, and though 11,700 less women of that age group were enrolled in 1999, men over the same time period ranged from 30,000 to 39,000 persons while women accounted for 49,000 to 61,500 (see table 1).
Table reference:
Table 1
Rate of Nursing Home Residence among People Age 65 or Older, by Sex and Age Group, 1985, 1995, 1997, 1999a
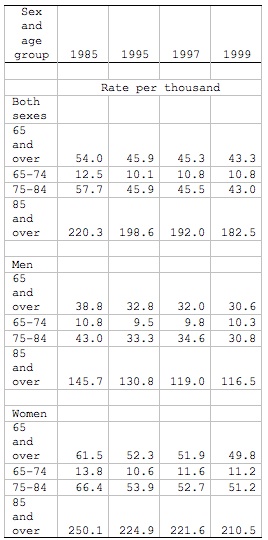
Example Table
Source: Federal Interagency Forum on Aging-Related Statistics, Older Americans 2008: Key Indicators of Well-Being, Federal Interagency Forum on Aging-Related Statistics, Mar. 2008, table 35A.
a. Note: Rates for 65 and over category are age-adjusted using the 2000 standard population. Beginning in 1997, population figures are adjusted for net underenumeration using the 1990 National Population Adjustment Matrix from the U.S. Census Bureau. People residing in personal care or domiciliary care homes are excluded from the numerator.
Figures
- All visuals/illustrations that are not tables or musical score examples (e.g. maps, diagrams, charts, videos, podcasts, etc.) are labeled Figure or Fig.
- Refer to the figure in-text and provide an Arabic numeral that corresponds to the figure. Do not capitalize figure or fig.
- MLA does not specify alignment requirements for figures; thus, these images may be embedded as the reader sees fit. However, continue to follow basic MLA Style formatting (e.g. one-inch margins).
- Below the figure, provide a label name and its corresponding arabic numeral (no bold or italics), followed by a period (e.g. Fig. 1.). Here, Figure and Fig. are capitalized.
- Beginning with the same line as the label and number, provide a title and/or caption as well as relevant source information in note form (see instructions and examples above). If you provide source information with your illustrations, you do not need to provide this information on the Works Cited page.
- If full citation information is provided in the caption, use the same formatting as you would for your Works Cited page. However, names should be listed in first name last name format.
Figure Example
In-text reference:
Some readers found Harry’s final battle with Voldemort a disappointment, and recently, the podcast, MuggleCast debated the subject (see fig. 2).
Figure caption (below an embedded podcast file for a document to be viewed electronically):
Fig. 2. Harry Potter and Voldemort final battle debate from Andrew Sims et al.; “Show 166”; MuggleCast; MuggleNet.com, 19 Dec. 2008, www.mugglenet.com/2015/11/the-snape-debate-rowling-speaks-out.
Musical Illustrations/"Examples"
- The descriptor "Example" only refers to musical illustrations (e.g. portions of a musical score). It is often abbreviated "ex."
- Refer to the example in-text and provide an Arabic numeral that corresponds to the example. Do not capitalize "example" or "ex" in the text.
- Supply the illustration, making sure to maintain basic MLA Style formatting (e.g. one-inch margins).
- Below the example, provide the label (capitalizing Example or Ex.) and number and a caption or title. The caption or title will often take the form of source information along with an explanation, for example, of what part of the score is being illustrated. If you provide source information with your illustrations, you do not need to provide this information on the Works Cited page.
Musical Illustration Example
In-text reference:
In Ambroise Thomas's opera Hamlet, the title character's iconic theme first appears in Act 1. As Hamlet enters the castle's vacant grand hall following his mother's coronation, the low strings begin playing the theme (ex 1).
Musical Illustration reference:
Ex. 1: Hamlet's Theme
Source: Thomas, Ambroise. Hamlet. 1868.
Source information and note form
Notes serve two purposes: to provide bibliographic information and to provide additional context for information in the text. When it comes to citing illustrations, using notes allows for the bibliographic information as close to the illustration as possible.
Note form entries appear much like standard MLA bibliographic entries with a few exceptions:
- Author names are in First_Name—Last_Name format.
- Commas are substituted for periods (except in the case of the period that ends the entry).
- Publication information for books (publisher, year) appears in parentheses.
- Relevant page numbers follow the publication information.
Note: Use semicolons to denote entry sections when long series of commas make these sections difficult to ascertain as being like or separate (see examples below.) The MLA Handbook (8th ed.) states that if the table or illustration caption provides complete citation information about the source and the source is not cited in the text, authors do not need to list the source in the Works Cited list.
For additional information, visit the MLA Style Center’s page on Using Notes in MLA Style.
Examples - Documenting source information in "Note form"
The following examples provide information on how a note might look following an illustration. Write the word “Source” immediately before your source note. If an illustration requires more than one note, label additional notes with lowercase letters, starting with a (see the note underneath the example table above).
Book
Tom Shachtman, Absolute Zero and the Conquest of Cold (Houghton Mifflin, 1999), p. 35.
Website (using semicolons to group like information together)
United States; Dept. of Commerce; Census Bureau; Manufacturing, Mining, and Construction Statistics; Housing Units Authorized by Building Permits; US Dept. of Commerce, 5 Feb. 2008; Table 1a.
In this example, the commas in Manufacturing, Mining, and Construction Statistics prompt the need for semicolons in order for the series information to be read easily. Even if Manufacturing, Mining, and Construction Statistics had not appeared in the entry, the multiple "author names" of United States, Dept. of Commerce, and Census Bureau would have necessitated the use of a semicolon before and after the title and between ensuing sections to the end of the entry.
Furthermore, the publisher and date in a standard entry are separated by a comma and belong together; thus, their inclusion here (US Dept. of Commerce, 5 Feb. 2008) also necessitates the semicolons.
Note on manuscripts
Do not embed illustrations (tables, figures, or examples) in manuscripts for publication. Put placeholders in the text to show where the illustrations will go. Type these placeholders on their own line, flush left, and bracketed (e.g. [table 1]). At the end of the document, provide label, number, caption, and source information in an organized list. Send files for illustrations in the appropriate format to your editor separately. If you provide source information with your illustrations, you do not need to provide this information on the Works Cited page.